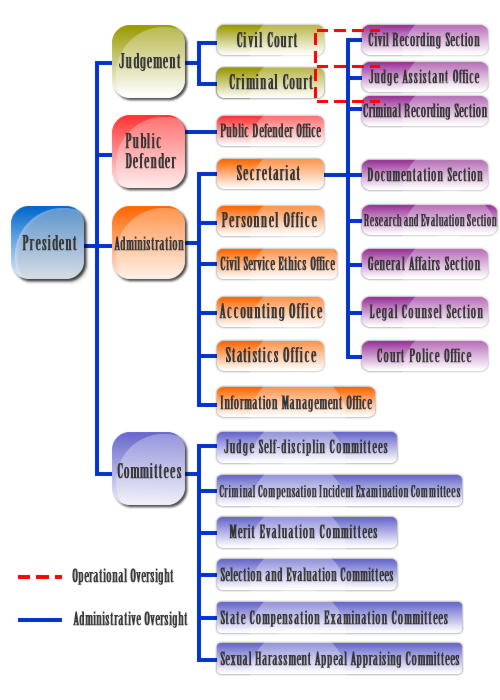
Organization
With a president to take charge of Court affairs, the Court is divided into two parts: Judgment and Administration, each of which is flanked by the following units and with the following responsibilities:
I. Judgment
1. The Civil Court and the Criminal Court conduct the appeal to the second instance of the civil or criminal case and the counter-appeal case under the system of collegial panels.
Civil Trial:
The Court has seven civil courts, each of which has one presiding judge and three judges to handle civil appeals of the second instance and counter-appeal cases under the system of collegial panels, but they do not deal with simple litigation.
Criminal Trials:
The Court has eleven criminal courts, each of which has one presiding judge and two or three judges to handle criminal appeals of the second instance and counter-appeal cases under the system of collegial panels as well as litigation of the first instance concerning civil strife, foreign aggression or violation of foreign relations.
Professional Courts:
Based on various needs, the Court sets the professional courts, such as Professional Court of Fair Trade Cases, Family Professional Court, Professional Court of International Trade, Maritime Professional Court, Professional Court of State Compensation, Professional Court of Anti-corruption, Professional Court of Intellectual Property Rights, Professional Court of Juvenile Delinquency, Professional Court of Serious Criminal Cases, Professional Court of Public Security, Professional Court of Fair Trade Act, Professional Court of Sexual Harassment, etc.
2. One assistant presiding judge assists the president in studying and reading the documents of the civil or criminal cases.
3. Two public defenders support defendants in specific cases of compulsory vindication.
II. Administration
1. Secretariat
This has one chief secretary to assist the president in handling general administration affairs. The Civil Records Section, Criminal Records Section, Documentation Section, General Affairs Section, Research and Evaluation Section, Litigation Counseling Section and Bailiff Office are located within it. They are in charge of judgment records, documents, general affairs, financial affairs, research and evaluation of work management and affairs, litigation assistance, prisoner control and protection as well as safekeeping respectively.
2. Personnel Office
This is responsible for appointing and dismissal and transfer of officials, rewards and punishment, assessments, evaluation of achievements, retirements, compensation, salaries, training, holiday and business trip management, personnel files management as well as matters concerning the material benefits of personnel, civil servant insurance, health insurance, cooperation and activities.
3. Civil Service Ethics Office
This is responsible for enactment and popularization of the civil service ethics regulations and rules, anti-corruption, prosecution affairs, suggestions on civil service ethics, assessments, rewards and punishment, protection of confidential affairs, property declarations and the other matters concerning civil service ethics.
4. Accounting Office
This is responsible for the arrangement of general estimates, budget and final accounts, approved budgetary distribution and projects, control of financial income and expenses, management of judicatory income, control of legal fees as well as for suggestions to enhance financial power and lower expenses.
5. Statistics Office
This is responsible for judicatory statistical affairs.
6. Information Management Office
This is responsible for the management and maintenance of the computers and network systems in the Court, installation of the applied systems, management of the operational documents and maintenance of files. It is the advice center for problems with computers in the Court.
- Release Date:2020-10-26
- Update:2020-10-26